What is bot mitigation? How can you detect and stop bad bots? And how does Queue-it help block and control bot traffic for successful peak traffic events? Find out in this comprehensive guide to bot mitigation.
Bad bots are the parasites of the internet. They exploit high-demand events, steal data, and prey on website users.
These parasites now make up one-third of all internet traffic. And with the rise of AI, their accessibility, sophistication, and volume is only growing.
In recent sales we’ve worked with, we’ve seen bot-to-human ratios of 20:1, automated attacks comprising of over 32 million requests, and a single person trying to simulate over 32,000 users.
Bot attacks like these are virtually impossible to detect and prevent in real time without robust bot mitigation. But what is bot mitigation? How can you detect and block bad bots? And how does Queue-it help major organizations block bots on their busiest days?
Table of contents
Bot mitigation is the act of blocking bad bots or malicious activity from websites or apps. It’s typically done using bot mitigation software, which are services that scan online traffic to identify suspicious activity and block or challenge it.
At its core, mitigating bots requires two key capabilities:
- Detection: Identifying bad actors, suspicious requests, or malicious activity.
- Action: The ability to block, challenge, slow down, or mitigate this malicious activity in some way.
By detecting and acting on bot traffic with bot mitigation, online businesses can:
- Preserve customer trust and loyalty: 35% of online businesses say bot attacks result in reputational damage, reduction in conversions, and data leaks.
- Reduce operational and support costs: Up to 80% of operational ecommerce costs are negatively impacted by bad bots.
- Keep websites & apps online: 45% of businesses say bot attacks are causing more website crashes.
There are hundreds of kinds of bots and hundreds of ways to detect them. Simple tactics include presenting CAPTCHA challenges, blocking known data centers, or rate limiting aggressive IP addresses. More sophisticated tactics involve complex algorithms and custom rules that scan dozens of signals to detect suspicious activity.
Let’s start with some simple, free methods you can use to check if you have a bot problem, then move to the more sophisticated detection tactics.
RELATED: Hype Event Protection: Queue-it & Akamai's Joint Solution to Stop Bots at Scale
- Look at traffic trends: The easiest way to check if there are bots on your site is with a free-to-use tool like Google Analytics. Check your analytics for abnormal surges in traffic coming from particular cities or regions, accessing particular pages, or arriving at abnormal hours. You can also look for anomalies in bounce rates, session durations, or user journeys.
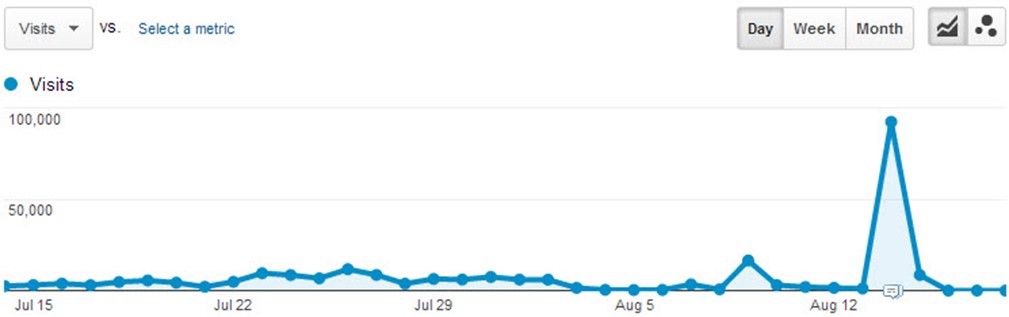
· Look at sales data: Another free way to check for bots is to run a post-sale audit after an event you suspect was targeted. Check for multiple transactions made with the same credit card, being shipped to the same address, or coming from the same account or IP address. Check for “address jigging” too, which scalpers use to create slight variations of the same address—for example, by adding a unit/apartment number to a house without multiple dwellings.
· Check social media & resale platforms: Do you suspect your inventory is being bought for resale purposes? Just search on social media or resale platforms for your products or tickets. You may find accounts selling dozens of your products for large mark-ups or even bragging about their activity to sell their own bot software.
If you see in your sales data, traffic trends, or online that you’re experiencing bot activity on your website, you’ll likely need bot detection and mitigation software to accurately identify bad actors before they get a chance to harm your business.
Bot mitigation software offers much more comprehensive analytics and detection methods than free tools like Google Analytics alone. Bot detection software will typically flag activity as suspicious or malicious through:
· Anomaly detection: Detecting and flagging abnormal access patterns, such as low latency, high rate of attempts, or abnormal user journeys.
· Reputation scores: Automatic scoring of IP addresses based on user behavior, past network activity, and other signals.
· Blocking known bots & data centers: Maintaining a list of known bots and data centers that are associated with malicious activity.
· Device fingerprinting: Looking at combinations of hardware, software, browser settings, and more to create a “fingerprint” for each device
· Behavioral analysis: Observing how visitors interact with via signals like mouse movements, click patterns, and typing behavior.
· Repeated requests from single IP: Identifying aggressive IP addresses by tracking rate or volume of requests.
· Visitor identification: Tying visitors to an “identity signal”, such as a login, promo code, email, or other unique identifier to enforce one session or transaction per visitor.
· Irregular or outdated user agents: Identifying bots via outdated user agents that are no longer used by regular human visitors.
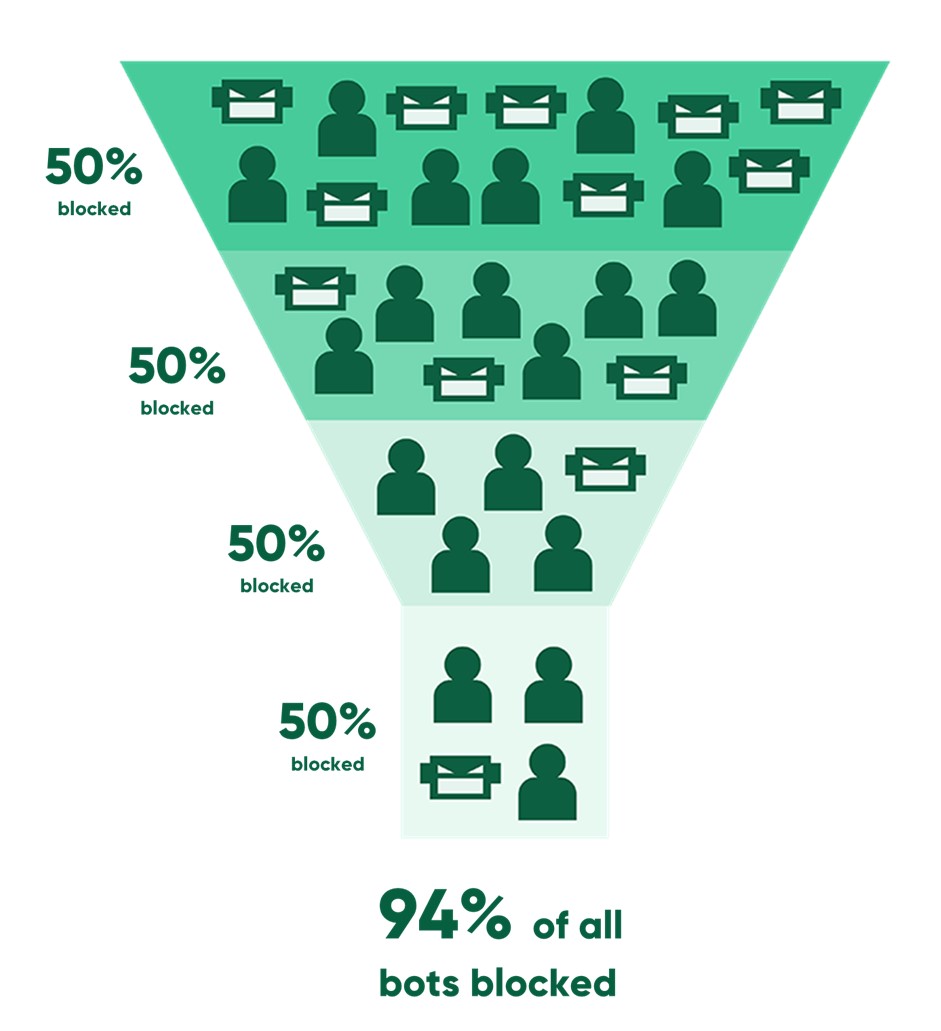
Bot mitigation tools detect bots in so many ways because the key to stopping bots is through a multi-layered approach. The more layers of detection and protection you use, the fewer bots can slip through the cracks.
For example, if you have four layers of bot detection that each identify 50% of bots, 10,000 bots become 5,000, then 2,500, then 1,250, then 625. In this scenario, the multi-layered approach removes 93.75% of bots, even with tactics that only manage to detect 50% of bots each.
To stop bot traffic on your website, you first need to identify the malicious or suspicious visitors, then have the tools to block, challenge, slow down, or deceive them.
In an ideal world, stopping bot traffic would just involve hard blocking all malicious activity on your site, app, or APIs. But the growing sophistication of bots makes it increasingly difficult to identify a bad actor with 100% certainty—which is why you need several tactics to mitigate bots.
· Block known bots: If you have 100% certainty that requests coming from a particular IP address, or ASN, or region is a bot, you can simply hard block that traffic.
· Challenge suspicious traffic: If a visitor shows both human and bot signals, it’s typically labelled “suspicious” and presented a challenge such as a CAPTCHA or Proof-of-Work Challenge. These challenges are easy for humans to solve, but difficult or impossible for bots to solve.
· Slow down traffic: A visitor making hundreds of requests may be a genuine frustrated customer who’s impatiently refreshing the page, or it could be a bot trying to get access to a new product at the first possible second. To mitigate this activity, whether it comes from a bot or a human, you can limit the frequency of requests with rate limiting or control the flow of traffic with a virtual waiting room.
· Deceive bots: Sometimes blocking a bot outright is the wrong approach, because it simply motivates them to try another attack using new methods. This is where deception and honeypots come in. You can redirect known bots to fake pages, trick them into purchasing the wrong items, or even charge them inflated prices.
Organizations choose between blocking, challenging, slowing, or deceiving bots based on their risk appetite, use case, and past experiences with bots. Most bot mitigation tools are designed to be highly customizable, allowing you to tailor your defense strategy to your needs.
At Queue-it, for example, bot mitigation is deployed via an IF-THEN framework in a tool called Traffic Access Rules. Organizations can configure up to 100 custom rules based on nine distinct parameters, such as ASN, IP address, Classifier, and Reputation score. If you wanted to challenge high risk visitors, block data center traffic, and whitelist internal IPs, you’d set up the following rules:
· IF [reputation score=high risk], THEN [Challenge traffic]
· IF [Classifier=Datacenter], THEN [Hard block traffic]
· IF [IP address=your company IP address], THEN [Bypass queue]
These rules are applied like a security checkpoint at an airport. Each visitor request is analyzed for these parameters, and is either blocked, challenged, or given access.
During a high-profile concert ticket sale, 95% of the total requests came from bots and uninvited visitors.
In just three hours, Queue-it identified 3.2 million untrusted visitors and blocked them from the sale page.
Queue-it helped the ticketing company identify and block this traffic in three key ways:
· Hard blocking data centers: The ticketing company set up Traffic Access Rules to hard block over 1.3 million requests coming from data centers.
· Invite-only Waiting Room: The ticketing company sent out unique, single-use invitation links to the concert ticket sale using Queue-it’s Invite-only Waiting Room. 138,000 invited users were verified via their unique link and given a position in the waiting room, while over 1 million were blocked due to invalid or re-used links. One scalper tried to open their link over 31,000 times but only got a single place in the waiting room.
· Challenging suspicious traffic: The ticketing company set up Traffic Access Rules to challenge suspicious traffic identified through Anomaly Detection and Reputation Scores, with 900,000 requests failing to solve a CAPTCHA challenge.
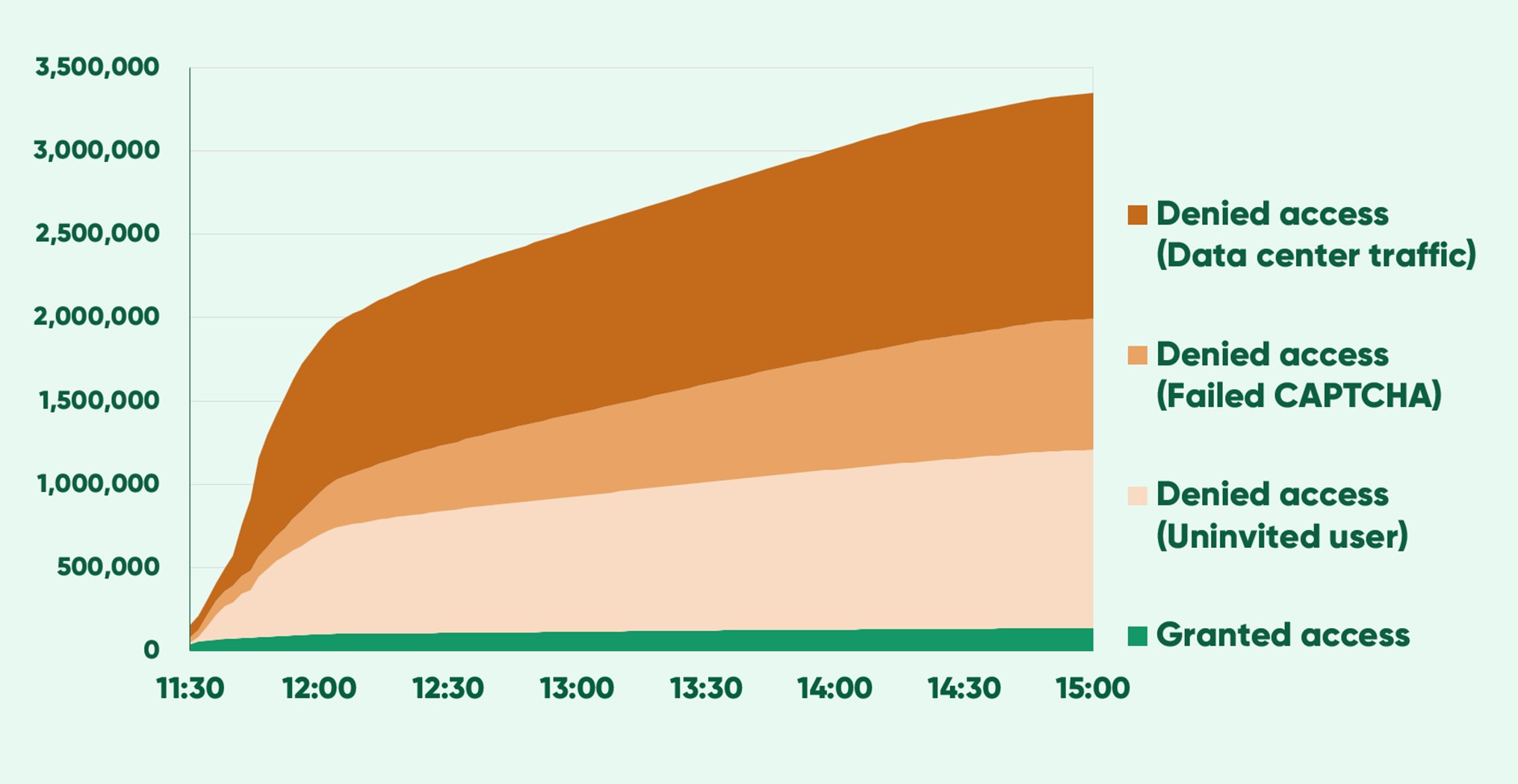
By blocking over 95% of traffic, this company ensured fair, exclusive access for 138,000 genuine fans. They dramatically reduced the load on their servers, as well as the wait time for genuine visitors.
RELATED: Behind-the-Scenes of an Onsale: How Queue-it Blocked 8.3 Million Ticket Bots
Queue-it is unique in the bot mitigation landscape because it offers a virtual waiting room solution with built-in bot protection tailored for high-traffic scenarios like ticket onsales or product drops. The virtual waiting room acts as a security checkpoint that controls the flow of traffic to protect your entire website, a specific landing page, or particular action like an API call or transaction.
This security checkpoint slows down and controls traffic, allowing you to run a series of bot checks on visitors before they hit your site or perform a protected action. It also enables you to prevent load-induced issues like crashes, slowdowns, and overselling by giving you control over the rate at which visitors hit your site or key bottlenecks.
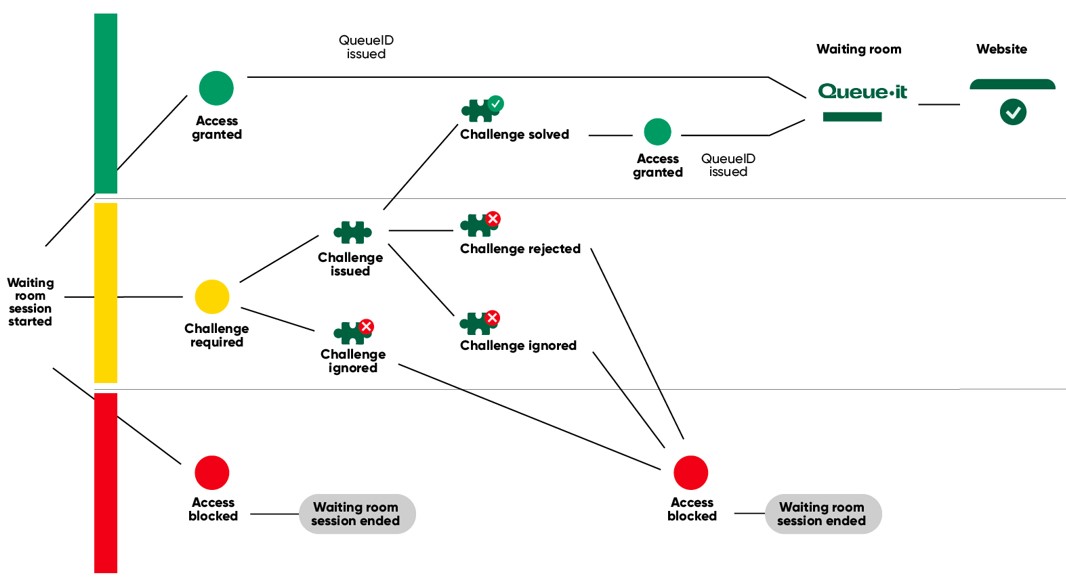
For robust bot protection and fairness during a high-demand event, Queue-it customers deploy multi-layered protection, distributed throughout the user journey, as shown in the image below.
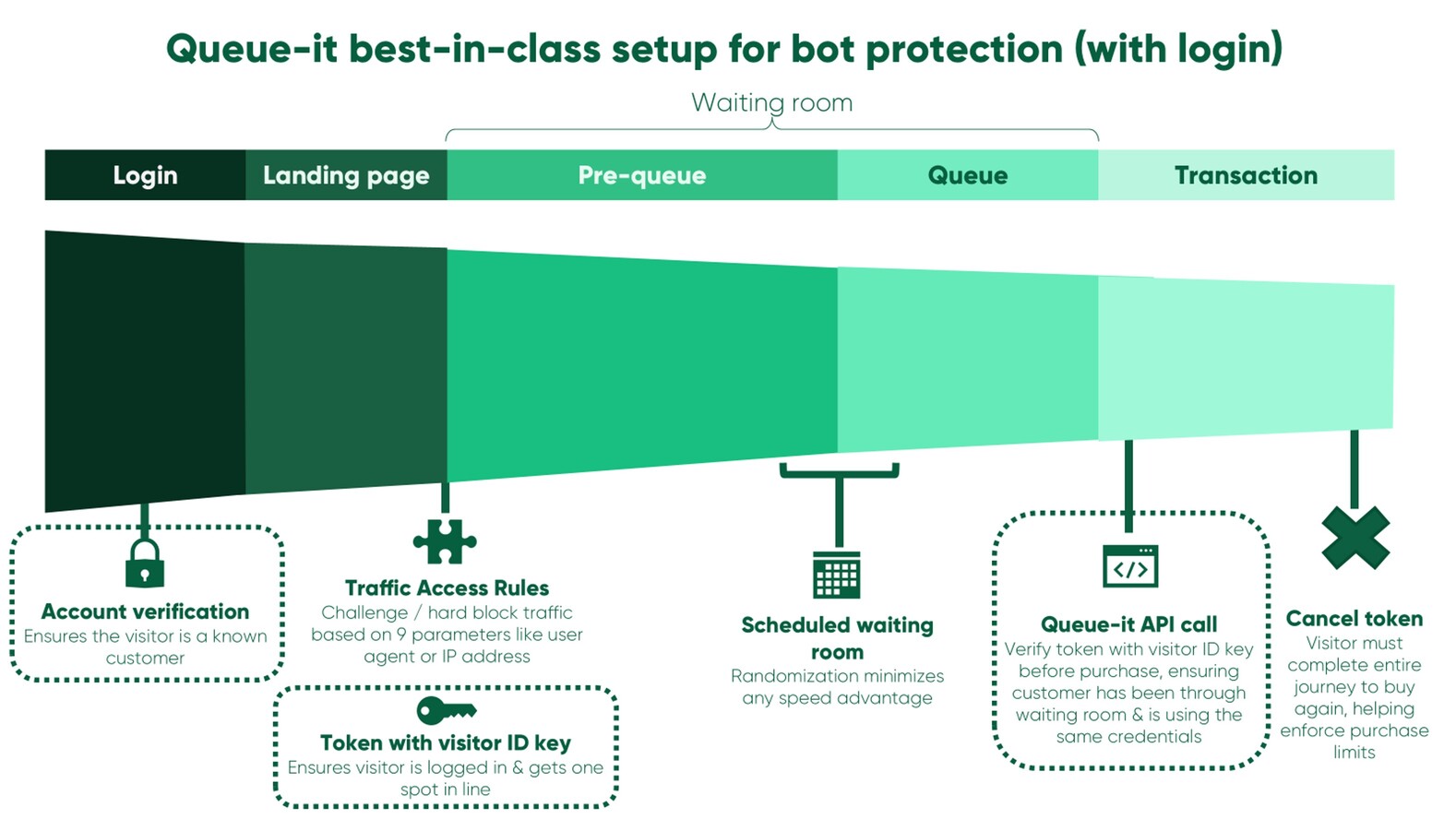
· Login: If you require visitors to log in before accessing your sale, you can tag all visitors with a Visitor Identification Token. This limits bots’ volume advantage by ensuring each known visitor can only get one place in the waiting room and allows you to validate visitors before transactions via Queue-it’s API.
· Landing page: After logging in, direct visitors to a landing page containing the link to the protected transaction page. All visitors following this link from this page get tagged with an Enqueue Token, which verifies that they’ve followed a normal user journey to access the queue.
· Pre-queue: Visitors following the link to the transaction page get flowed to a pre-queue, which is a holding page with a countdown timer to the start of the event. As visitors try to access the pre-queue, Queue-it checks their Visitor Identification Token and Enqueue Token to ensure they’ve followed the correct path and get only one spot in line per known visitor. Your Traffic Access Rules are applied to all visitors in the pre-queue—enabling you to block or challenge visitors identified as suspicious or malicious via a set of tailored rules.
· Queue: When the pre-queue timer hits zero and the event starts, all visitors get randomized, just like a raffle, and flowed to the queue in their randomly assigned positions. This randomization process removes the speed advantage bots typically rely on during limited-inventory sales, ensuring a level playing field for all visitors. After the event has started, visitors access to the queue in first-in, first-out order—the gold standard for fairness.
· Transaction: Visitors get flowed from the queue to the transaction page in fair order and at the rate you choose. Then, as the visitor is checking out, you can make an API call to Queue-it to verify the Visitor Identification Token, ensuring one purchase per known visitor and that every visitor has passed through the queue before they make their purchase.
· End session: On the order confirmation page, you can trigger a cancel action, which cancels their session validity. This means that if the visitor wants to transact again, they’ll need to return to the back of the queue.
If you don’t have login or want to avoid requiring login for users, you can achieve a similar visitor journey using the Invite-only waiting room. In this scenario, you can verify visitor’s identity using unique, single-use links, or via two-factor authentication of their emails, which is handled by Queue-it.
By enforcing this user journey for your high-demand events, you achieve:
· Fair, orderly, and informed access for all visitors
· Remove the speed and volume advantage bots rely on
· Prevent load-induced site crashes, payment errors, and overselling
· Limit purchases to one per verified customer
· Ensure bots cannot bypass standard user journey
At its core, mitigating bots requires two key capabilities:
- Detection: Identifying bad actors, suspicious requests, or malicious activity.
- Action: The ability to block, challenge, slow down, or mitigate this malicious activity in some way.
By detecting and acting on bot traffic with bot mitigation, online businesses can:
- Preserve customer trust and loyalty: 35% of online businesses say bot attacks result in reputational damage, reduction in conversions, and data leaks.
- Reduce operational and support costs: Up to 80% of operational ecommerce costs are negatively impacted by bad bots.
- Keep their websites online: 45% of businesses say bot attacks are causing more website crashes.