The Queue-it virtual waiting room acts as a security checkpoint that filters and throttles visitors before they reach your origin. This makes it a powerful control layer for mitigating bots and abuse.
Queue-it includes several bot and abuse management capabilities that you can use alongside with your existing protection stack to strengthen defenses and ensure a fair, stable user experience.
Bot and abuse mitigation is a cat-and-mouse game with no single silver bullet. Effective protection requires multiple, complementary layers.
Queue-it works alongside your existing WAF, rate-limiting, and bot-detection tools—not instead of them.
- WAFs and rate-limiters excel at slowing or blocking clear spikes of malicious traffic. But during legitimate demand spikes—like ticket onsales or product drops—human traffic can look identical to bot traffic in volume and behavior. Traditional tools see a flood of requests; Queue-it sees a surge of customers that need orderly access.
- Bot detection engines rely on telemetry and behavioral data. Fast bots often complete their tasks before detection logic has enough signals to classify them. Queue-it complements these tools by regulating the flow of visitors, giving the tools more time and telemetry to make better decisions while protecting the user experience for real visitors.
Think of Queue-it like an airport security checkpoint: it doesn’t replace other security layers, but it’s where the flow of passengers is managed so credentials can be verified and additional checks can occur. Queue-it serves the same function in your online traffic flow—ensuring orderly, fair, and secure access even under extreme load.
We define “malicious traffic” as traffic coming from bots or users that try to unfairly access your website or app.
Bot or script traffic may include:
- Off-the-shelf bots
- Custom-built applications
- Curl / wget command line scripting
- Headless browsers
- Brute force attempts trying to avoid the queue/guess the target URL
Malicious user behavior may include:
- Obtaining multiple places in line via multiple browsers / devices
- Trying to bypass the waiting room by avoiding invoking the queue logic
- Waiting their turn and then sharing sessions/cookies with others so they don’t have to wait
- Disabling cookies / AJAX calls to Queue-it to avoid invoking the queue logic
Malicious traffic can have real, negative consequences for your business, as research shows:
- Website crashes: Malicious traffic adds extra load, which could cause your website and app to slow or crash
- Faulty analytics: Bots can skew key data points like cart abandonment rates or customer base size, clouding up the reporting you need to make informed business decisions.
- Increased operational & support costs: 80% of operational costs are negatively impacted by bots, and bots cost enterprises over $85 million annually
- Harmed brand reputation & loyalty: Genuine shoppers view shopping bots snapping up most or all available product as incredibly unfair, will lose faith in your brand and move on to others where they feel valued.
Bots and malicious users operate using their speed and volume advantages to unfairly access your site. Scripted bots use their speed advantage to enter a site milliseconds after the start of a sale and quickly advance past human users to the checkout page. When done at scale, these bots can come away with a massive amount of product.
When there's a waiting room in place, bots and malicious users try to gain an unfair advantage by using one or several of these strategies:
- Bypassing the waiting room (i.e. navigating directly to the target URL and skipping ahead of others in line)
- Using speed to get the best possible queue number
- Obtaining multiple queue numbers, for example by using many unique sessions on different devices to have several places in line and a better chance of scoring product
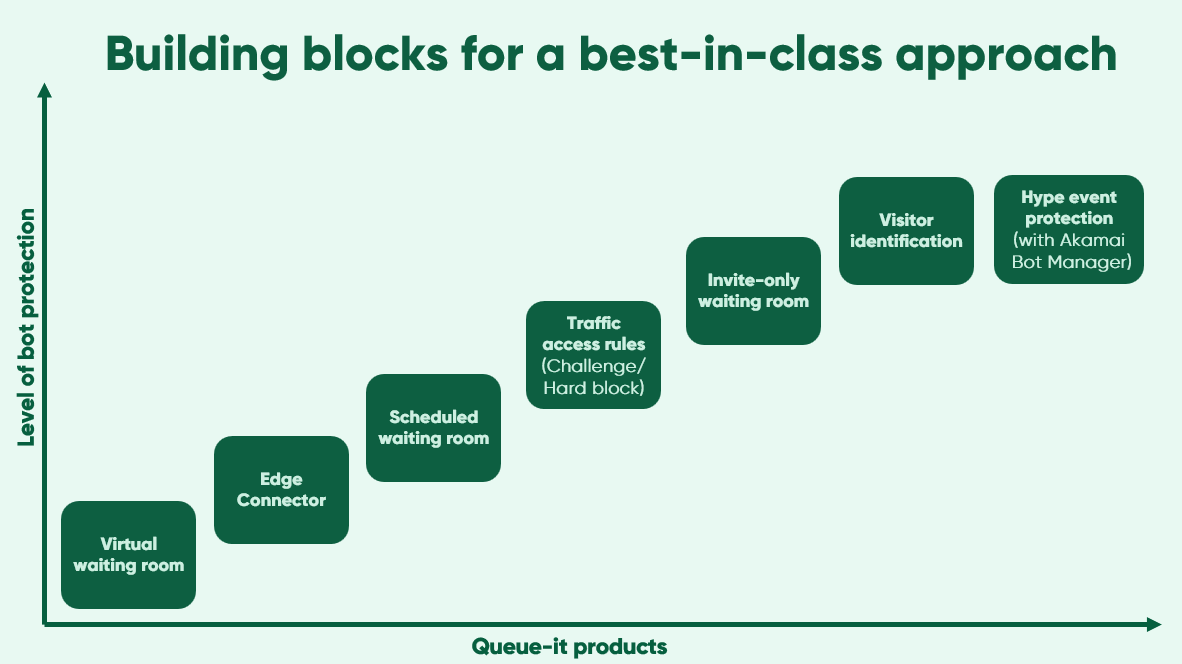
Queue-it's virtual waiting room is an important control layer in a multilayered bots and abuse setup. But Queue-it itself also contains several layers of protection that can be combined for a more hardened setup.
Here is a list of steps you can take with Queue-it to prevent bots and abuse, from the simple to the sophisticated.
For a full explanation of Queue-it's most hardened setup against bots, and the steps to get there, watch the Block bad bots: Best practices for high-demand events product talk.
Integrate Queue-it using a server-side or edge Connector to ensure visitors don't bypass or block the queue. A client-side integration is vulnerable to visitors manipulating the JavaScript code to skip the line and is not suitable where bots/abuse are a concern.
Queue-it offers 20+ Connectors for the edge, server-side, native mobile apps, and ecommerce platforms. A skilled developer can typically configure one in a day.
To learn more about integration options, visit our Queue-it Connectors page.
Bots use their speed advantage to beat out genuine customers. If a sale started at 10 a.m. and a first-come, first-served waiting room opened right at 10:00:00, speedy bots would arrive en masse exactly at that millisecond and beat out genuine customers.
A scheduled waiting room neutralizes the speed advantage by using randomization. All visitors who arrive before a timed sale or registration starts are placed in a pre-queue, where they're shown a countdown to the start time. When the sale or registration begins, everyone in the pre-queue is randomized and assigned a place in the online queue. This means everyone's given an equal shot at a good spot in queue--as long as they arrived on time.
The scheduled waiting room has the added benefit of offloading early visitors from your infrastructure, preventing eager customers from overwhelming your site or app before the sale even begins.
To learn more about setting up a scheduled waiting room, get the Technical Integration white paper. To understand more about why Queue-it recommends a blend of first-come-first-served and randomization for the most fair events, you can read our blog post.
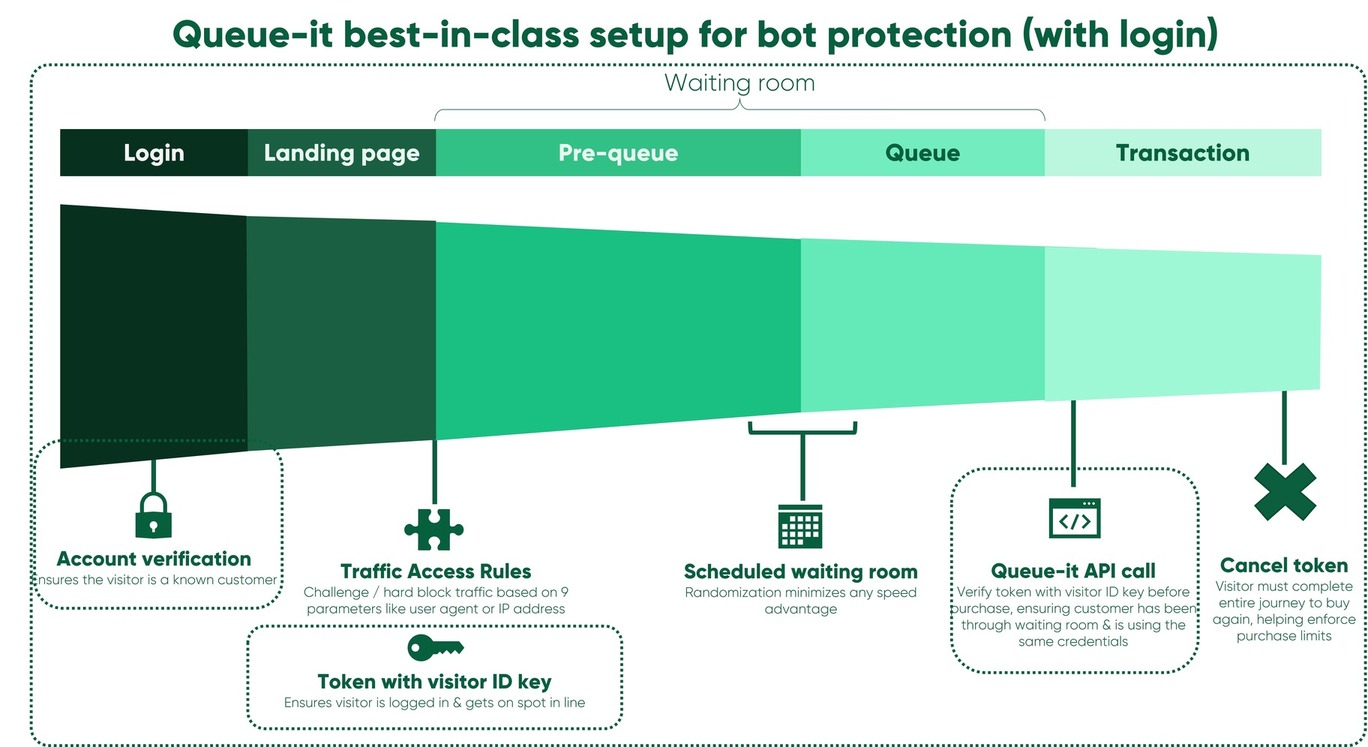
Traffic Access Rules lets you identify a segment of visitors and choose to challenge, block, or allowed them to bypass the queue.
Visitor segments can be based on static network analysis (like IP address, ASN, or user agent) and user behavior (like reputation score), and challenges can include Proof-of-Work challenges or CAPTCHAs.
Rules work like IF-THEN statements with ANY/ALL operators. For example:
- IF [reputation score=high risk], THEN [Challenge traffic]
- IF [IP address=your company IP address], THEN [Bypass queue]
- IF [Classifier=Queue-it Datacenter], THEN [Hard block traffic]
Traffic Access Rules gives you more control and flexibility over how you handle traffic, so you can tailor your bots and abuse protection to your needs.
To learn more about Traffic Access Rules, read our product update.
Queue-it's Invite-only waiting room is a scheduled waiting room with a zero-trust approach to security. You decide who may enter the queue and verify that people joining are known customers. This feature provides secure control over access and blocks unwanted traffic, making Invite-only waiting rooms suitable for exclusive or early access sales and for rewarding VIP visitors.
To decide which customers can access the queue, upload a list of which customers can gain access by creating links with unique identifiers—e.g., email addresses or member IDs—distributed via email or their account page. When visitors access the waiting room, Queue-it verifies their identities against the pre-uploaded “visitor identity list” and 2FA code when applicable. Only visitors with a verified identity will be granted access to the Invite-only waiting room and subsequently the protected website or application.
This lets you proactively validate genuine customers instead of finding and blocking countless bots.
To learn more about setting up an Invite-only waiting room, visit the product update blog and get the Invite-only white paper.
Visitor identification lets you block malicious traffic and bad bots prior to them entering the waiting room. With a visitor identification key and an enqueue (enter-queue) token, you can determine which visitors are genuine and can move forward.
Visitor identification keys are any data point that can be used to identify a visitor, such as an account ID, email address, or promo code. The enqueue token is a vehicle for transmitting visitor identification keys between your application and Queue-it. The token is signed and encrypted so that it can’t be altered as it’s passed from one system to another. Linking waiting room entry to a physical identification or controlled virtual ID in this way is a powerful method of combating bots and abuse.
You have the option to enforce uniqueness on visitor identification keys (i.e. each ID is only allowed one place in the waiting room) and to require an enqueue token to enter the waiting room, meaning that visitors cannot share entry with others.
You put these tools into practice in several ways. For instance, you can assign an enqueue token only for visitors who’ve logged into your system. Or, only for those who’ve received a personalized link via email.
To learn more about controlling who enters your waiting room, read our product update.
After visitors exit the waiting room, you can add an additional level of security by verifying that the visitor has a valid enqueue token and has been through the waiting room (i.e. didn’t find a way to bypass the waiting room).
For instance, when visitors try to complete a transaction you can call the Queue-it API to verify that they have a valid enqueue token before they’re allowed to complete their transaction. Alternatively, you can allow visitors to complete the transactions unimpeded and verify the transaction was associated with a valid enqueue token before you ship their order.
While validating visitors who’ve exited the waiting room requires more complex setup on your end, it creates a reinforced, enclosed flow where only desired visitors enter the waiting room and only those who’ve passed through the waiting room can complete transactions.
The diagram below illustrates the most hardened Queue-it setup when protecting a user journey behind a login. The visitor identification key ties the login details to entry in the waiting room, which is then cross-referenced upon purchase to ensure only verified customers who've been through the queue and are using their own credentials may complete their purchase.
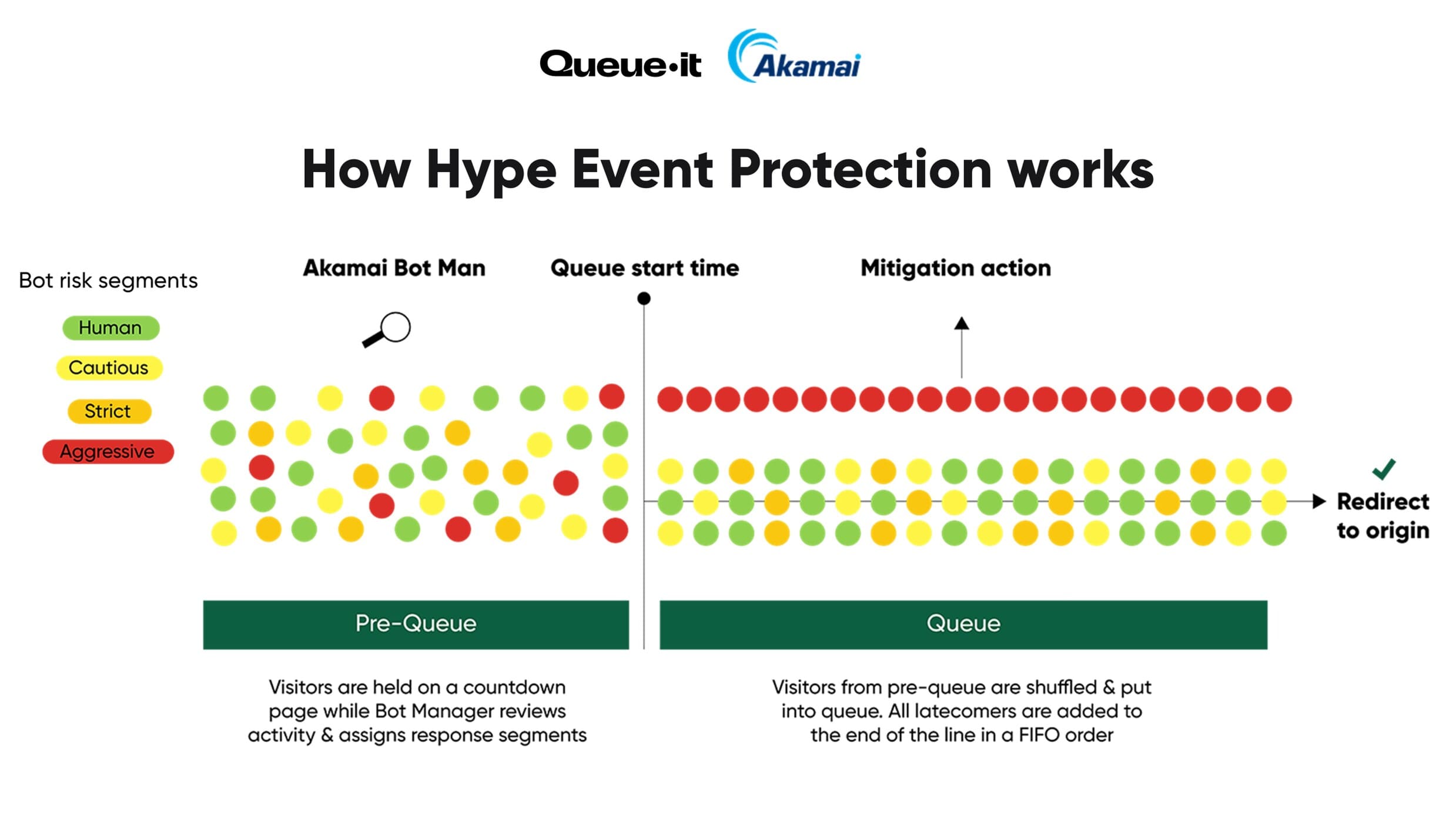
Hype Event Protection combines Akamai’s advanced bot detection with Queue-it’s waiting room to neutralize bots’ speed and volume advantage—while keeping the experience seamless for real customers.
All sale traffic flows through the Hype Event Protection waiting room, which serves as a security checkpoint for sale access. While the waiting room is in pre-queue mode, Akamai Bot Manager conducts enhanced detection using extended telemetry and user behavior data. Bot Manager assigns bots a segment, but no mitigation takes place yet. This prevents botters from quickly retooling and forces them to use significant compute resources to keep many bots in the pre-queue.
At the start of the queue phase, visitors marked as “Aggressive” are mitigated—hard blocked or forced to re-join at the end of the line. All other genuine visitors are randomized and placed into the online queue, ensuring fair sale access and minimized wait times.
To learn more about Hype Event Protection, read our product update.